|
|
 Navigation par listes
Navigation par listes
|
| Page de départ | Partonomie TAH |
| Niveau supérieur |
système nerveux central  Abrégé étendu Abrégé étendu
|
| Niveau actuel |
encéphale  étendu étendu
|
| Langage subsidiaire avec le latin |
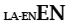 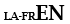 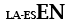
|
| Language principal non Latin |
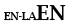  
|
 Liste partonomique
Liste partonomique
|
 Notes scientifiques
Notes scientifiques
|
| UID |
Libelle of note
|
| 5263 |
The Diencephalon in its classic, columnar view was divided into four dorsoventrally arranged columns separated by ventricular sulci: the Epithalamus, the Dorsal thalamus, the Ventral thalamus and the Hypothalamus. Extensive embryological studies made it clear that the thalamic 'columns' are derived from transversely oriented zones, the Prosomeres (see TE). Currently, the (Caudal) Diencephalon is subdivided into three segmental units, which from caudal to rostral, contain in their alar domains the Pretectum (prosomere 1 or P1), the Epithalamus and the Thalamus (P2) and the Ventral thalamus or Prethalamus (P3). The diencephalic basal plate contains the rostral part of the Substantia nigra-VTA complex and some other nuclei, collectively forming the Diencephalic or Prerubral tegmentum between the Mesencephalon and the Hypothalamus. The entire Hypothalamus or Rostral diencephalon arises from the alar and basal components of the secondary prosencephalon. The Preoptic area is one of the subpallial developmental domains (Puelles L, Harrison M, Paxinos G, Watson C 2013 A developmental ontology for the mammalian brain based on the prosomeric model. Trends Neurosci 36:570-578).
|
| 5265 |
The brain stem is composed of the midbrain (mesencephalon) and the hindbrain (rhombencephalon). The hindbrain was traditionally divided into the metencephalon (pons and cerebellum) and the myelencephalon or medulla oblongata. During development, the brain stem is segmentally organized. The midbrain is derived from two mesomeres, the isthmus from the isthmic rhombomere (rhombomere 0), and the hindbrain is composed of 11 rhombomeres. The cerebellum arises from the alar plates of the rhombomeres 0 and 1. The rostral hindbrain is derived from the rhombomeres 0 to 6, whereas the caudal hindbrain is derived from the rhombomeres 7 to 11.
|
 Signature
Signature
|
| Type of list | P2 |
| List Unit Identifier | 5257 |
| Sublist 1 | 5261 mesencephalon 355/166 on 8.4.2019 |
| Sublist 2 | 5263 diencephalon 399/180 on 30.12.2021 |
| Sublist 3 | 5264 telencephalon 1779/704 on 13.12.2020 |
| Sublist 4 | 5431 pons 40/23 on 11.6.2019 |
| Sublist 5 | 5686 cerebellum 331/160 on 15.4.2019 |
| Sublist 6 | 5779 hypothalamus 141/72 on 26.3.2019 |
| Sublist 7 | 11865 rhombencephalon rostrale 339/162 on 30.11.2020 |
| Sublist 8 | 11874 rhombencephalon caudale 528/227 on 2.4.2025 |
| Subtotals | subchildren 3912 subunits 1694 |
| Proper children | 12 |
| Number of children | 3924 (validated) |
| Proper units | 5 |
| Number of units | 1699 (validated) |
| Signature | 21090 (validated since 3.4.2025) |
| Date: 18.07.2025 |


